SERVLET
SERVLETS
- What is a servlet?
- Java Servlet is server side technologies to extend the capability of web servers by providing support for dynamic response and data persistence.
- The
javax.servletandjavax.servlet.httppackages provide interfaces and classes for writing our own servlets. - All servlets must implement the javax.servlet.Servlet interface, which defines servlet lifecycle methods.
- When implementing a generic service, we can extend the GenericServlet class provided with the Java Servlet API.
- The HttpServlet class provides methods, such as doGet() and doPost(), for handling HTTP-specific services.
- Most of the times, web applications are accessed using HTTP protocol and that’s why we mostly extend HttpServlet class. Servlet API hierarchy is shown in the below image.
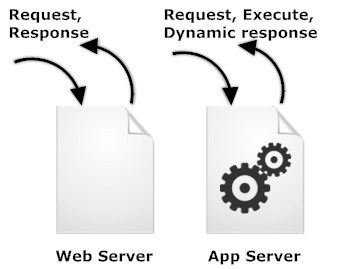
| S.NO | WEB SERVER | APPLICATION SERVER |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Web server encompasses web container only. | While application server encompasses Web container as well as EJB container. |
| 2. | Web server is useful or fitted for static content. | Whereas application server is fitted for dynamic content. |
| 3. | Web server consumes or utilizes less resources. | While application server utilize more resources. |
| 4. | Web servers arrange the run environment for web applications. | While application servers arrange the run environment for enterprises applications. |
| 5. | In web servers, multithreading is not supported. | While in application server, multithreading is supported. |
| 6. | Web server’s capacity is lower than application server. | While application server’s capacity is higher than web server. |
Some of the differences between ServletConfig and ServletContext are:
2.What is CGI and what are its drawbacks?
Ans: CGI stands for Common Gateway Interface which is a set of codes written on the server side that is used to interact through the Web Server with a Client running on a web server.
It takes the incoming request and for every new request, it starts a new process.
Drawbacks of Common Gateway Interface:
3) What are the advantages of Servlet over CGI?
Ans: The advantages of the servlet are as follows:
#4) How is a Servlet implemented in code?
Ans: Servlet can be implemented in code by simply extending the Httpservlet or generic servlet class.
#5) What is the difference between the Http Servlet and Generic Servlet?
Ans: Generic Servlet can handle all type of requests. As it has a service () method, it is independent, whereas Http Servlet extends the generic servlet and supports the HTTP methods such as doGet (), doPost (), doHead (), doTrace () etc.

#6) What are the life cycle methods of the Servlet?
Ans: There are basically three lifecycle methods of a servlet which are as follows:
#7) Explain the Lifecycle of Servlet.
Ans: The life cycle of a servlet is explained with reference to the below diagram.
Syntax: public void Init ()
Syntax: public void service ()
Syntax: destroy ()
Servlet Flow Diagram

#8) What is a web container and what is its responsibility?
Ans: A web container which is also called as Servlet container is used to interact with the Servlet and contains all the Servlet, JSP, xml files in it.
Web container manages the life cycle of a servlet and helps to map the URL to a specific servlet. Web container creates the object of a servlet.
#9) How is the Get () method different from the Post() method?
Ans: The reasons why Get () method is preferred over the Post() method are given below.
Get () method:
Post () method:
#10) What is Servlet looping or chaining?
Ans: Servlet looping is a process in which the output of one servlet is given as an input to another servlet and the last servlet output is considered as the actual output which is provided to the client.
This process is achieved through request dispatcher interface.
|
1) How many objects of a servlet is created?
Only one object at the time of first request by servlet or web container.
2) What is the life-cycle of a servlet?
- Servlet is loaded
- servlet is instantiated
- servlet is initialized
- service the request
- servlet is destroyed
3) What are the life-cycle methods for a servlet?
| Method | Description |
|---|---|
| public void init(ServletConfig config) | It is invoked only once when first request comes for the servlet. It is used to initialize the servlet. |
| public void service(ServletRequest request,ServletResponse)throws ServletException,IOException | It is invoked at each request.The service() method is used to service the request. |
| public void destroy() | It is invoked only once when servlet is unloaded. |
4) Who is responsible to create the object of servlet?
The web container and servlet container.
5) When servlet object is created?
At the time of first request.
6)WHAT IS DIFFERENCE BETWEEN GET and POST?
| Get | Post |
|---|---|
| 1) Limited amount of data can be sent because data is sent in header. | Large amount of data can be sent because data is sent in body. |
| 2) Not Secured because data is exposed in URL bar. | Secured because data is not exposed in URL bar. |
| 3) Can be bookmarked | Cannot be bookmarked |
| 4) Idempotent | Non-Idempotent |
| 5) It is more efficient and used than Post | It is less efficient and used |
7) What is difference between PrintWriter and ServletOutputStream?
- PrintWriter is a character-stream class where as ServletOutputStream is a byte-stream class.
- The PrintWriter class can be used to write only character-based information whereas
- ServletOutputStream class can be used to write primitive values as well as character-based information.
8) What is difference between GenericServlet and HttpServlet?
- The GenericServlet is protocol independent whereas
- HttpServlet is HTTP protocol specific.
- HttpServlet provides additional functionalities such as state management etc.
9)What is a web container and what is its responsibility?
Ans: A web container which is also called as Servlet container is used to interact with the Servlet and contains all the Servlet, JSP, xml files in it.
Web container manages the life cycle of a servlet and helps to map the URL to a specific servlet. Web container creates the object of a servlet.
#9) How is the Get () method different from the Post() method?
Ans: The reasons why Get () method is preferred over the Post() method are given below.
Get () method:
- Here a specific amount of data or information can be sent as the data is sent through the header.
- In Get() method, data is not secured as it is exposed in the URL bar to the user.
- Get () method can be bookmarked.
- Generally, get () method is more effective and used over the post () method.
Post () method:
- Here a huge amount of data or information can be transferred as the data is sent through the body.
- As the data in the Post () method is sent through the body, it is secured.
- Post () method cannot be bookmarked.
- Generally, the Post () method is less effective and is not often used.
#10) What is Servlet looping or chaining?
Ans: Servlet looping is a process in which the output of one servlet is given as an input to another servlet and the last servlet output is considered as the actual output which is provided to the client.
This process is achieved through request dispatcher interface.
#11) How will two or three servlets interact or communicate with each other?
Ans: There are two processes in which the servlets can communicate with each other.
a) Request Dispatcher Interface
b) Servlet Chaining
#12) Explain Request Dispatcher and its methods.
Ans: Request Dispatcher creates an object that is responsible to receive requests from the browser or client and then navigates them to any resources like Servlets, JSP, or HTML which resides at the server side.
There are basically two methods of Request Dispatcher:
a) Forward () method:
- In Forward() method the client sends the request to the Servlet1.
- The Servlet1 processes the request and then forwards the request to Servlet2.
- The servlet2 processes the request and generates a response which in turn is sent back to the client as the final response.
b) Include () method:
- In Include () method the client sends the request to the Servlet1.
- The Servlet1 processes the request and then includes the request and sends the request to Servlet2.
- The servlet2 processes the request and again sends it back to Servlet1 and
- The Servlet1 generates a response which in turn is sent back to the client as the final response.
#13) What is the use of Send Redirect () method?
Ans: Send Redirect () method which works at the client side is used to redirect the response to another resource like Servlet, JSP, HTML.
Syntax: void send Redirect(URL);
Example: response.sendredirect(“http://www.google.com”);
#14) How Forward () method is different from Send Redirect () method?
Ans: Forward () method:
a) It is used to send the exact same request to another resource.
b) It works on the server side within the server.
Send Redirect () method:
a) It always sends a new request to the resources as it uses URL.
b) It works at the client side both outside and within the server.
#15) Explain the WAR file?
Ans: A WAR file is basically referred to as a Web Archived file, which has all the files of your application like xml, servlets, JSP, HTML, configuration files combined into a single file so that deploying the application would be simple and easy.
It is advisable to use a WAR file for deployment.
#16) What do you mean by Servlet Context?
Ans: Servlet Context is basically referred to as an object which has information regarding application and the Web Container. With Servlet context we can log events, get the URL of the specific resource, and can easily store the attributes for other servlets to use.
The core advantage of Servlet is that it is easy to maintain and acts as a mediator between the container and servlet.
There are some important methods of servlet context which are given below:
a) getInitParameter () – return the value of parameter.
b) getInitParameterNames () – returns the name of parameter.
c) void setAttribute () – used to set the values of attributes.
d) void getAttribute () – used to get the values of attributes.
e) void removeAttribute () – used to remove the attribute.
#17) What exactly are the functions of Servlet?
Ans: The functions performed by the servlets are as follows:
a) Firstly Servlets receives the HTTP request which is sent from the client side.
b) Reads the request and extracts the data from the request.
c) After extracting the information, the servlets perform a business logic operation by accessing a database or invoking EJB's.
d) Lastly, it generates a response and sends it to the client in the form of HTTP or sends the response to the JSP page.
#18) What do you mean by deployment descriptor?
Ans: WEB.XML is said to be the deployment descriptor in a servlet.
It is the entry point for any application and possesses the welcome file list.
It defines resources, information about which servlet will be used and maps the servlet to URL.
#19) Explain Session tracking and its importance?
Ans: Session tracking is a process in which the data of the client or user can be maintained.
As every time a new request comes to the server, the server is unable to recognize that the new request is coming from the same client, to avoid this problem session tracking technique is used.
Session Tracking plays a vital role to recognize the client or the request.
#20) What are the different Session Tracking Techniques?
Ans: There are basically four types of techniques which are given below:
a) Cookies: Cookies are small information which is added to multiple client requests.
E.g: One request comes to the server, the server adds some cookies with the response, now when again the same client sends the request to the server, the server recognizes the user.
b) Hidden Form Field: Here we use a hidden text field for maintaining the state of the user.
c) URL Rewriting: Here we give an extra link for the next servlet to be mapped.
d) Http Session: Here a specific ID is generated for each user, so a server can recognize the user.
#21) What are the Servlet events?
Ans: Events are nothing but occurrences. Even changing the condition of the object is also an event.
The event classes and interface are as follows:
Classes: ServletRequestEvent, ServletContextEvent, HttpSessionEvent etc.
Interfaces: ServletRequestListner, ServletContextListner, HttpSessionListner etc.
#22) What do you mean by a filter and how does it work?
Ans: Filter is basically used to filter out things.
In a similar manner Filter in servlet is an object that is introduced at pre-processing of request and post-processing of request.
Its major functions include conversion, encrypt and decrypt values, input validations on data captures the IP address, and saves all the incoming request.
A filter is defined in web.xml and it can be removed from the web.xml so that there is no need to change the servlet resulting in cost reduction.
Diagram of servlet filter working

#23) Explain load on start-up and its importance?
Ans: Load on start-up is an element defined in web.xml (deployment descriptor) which helps the servlet to load at the time of deployment while the server is restarting.
The reason to use load on start-up is as the servlet is loaded on the first request received so initially it takes more time to load resulting decreased efficiency if we define loan on start-up is loads the servlet while server restarting which increases efficiency.
Load on start-up is also working on two values:
Positive (0,1,2,3….): The lowest positive value will be loaded first.
Negative: The servlet will be loaded when the first request is received.
#24) Is servlet synchronized?
Ans: No, the servlets are not synchronized. If we want to make servlet synchronized, we must implement SingleThreadInterface.
#25) What do you mean by Scope Object and what are its types?
Ans: Scope objects help to share information among web components via setattribute() and getattribute().
Types of Scope Objects are:
- Web Context
- Session
- Request
- Page
#26) What does the term Localization refer to?
Ans: Localization basically refers to the local tradition or language followed by the user. So, we add resources or elements to the particular website like adding the Hindi language so every user can understand.
#27) If servlet receives multiple requests, how many objects will it create?
Ans: Servlet will create only one instance, no matter how many incoming requests it receives.
#28) What is the major difference between Servlet and Applet?
Ans: The major difference between Servlet and Applet is that the Servlet resides on the Server side whereas the Applet resides on the client side in the web browser.
#29) Is it possible to have a Constructor inside the Servlet?
Ans: Yes, it is possible to define a constructor inside a servlet, but it can be called only by Servlet container and not explicitly.
#30) Name the packages that work with Servlet?
Ans: There are basically two packages which work with Servlet as shown below:
- Javax.servlet
- Javax.servlet.http
#31) What are the kinds of HTTP requests?
Ans: Kinds of HTTP request include:
- Get
- Post
- Head
- Options
- Put
- Trace
- Delete