HTML
HYPERTEXT MARKUP LANGUAGE
- What is HTML?
- HTML is a widely used language that gives our webpage a structure.
- HTML stands for HYPERTEXT MARKUP LANGUAGE.
- HTML was created by Berners lee in 1991.
- A markup language is a set of markups tags. Every webpage is created in HTML. HTML documents are described by HTML tags.
- It is a language of the World Wide Web. It is a standard text formatting language which is used to create and display pages on the Web.
- HTML makes the text more interactive and dynamic. It can turn text into images, tables, links.
- HTML pages are saved by adding .html or .html in web page name.
2.What is the difference between HTML elements and tags?
| Elements | Tags |
The element is an individual component of the HTML web page or document. It represents semantics or meaning. For example, the title element represents the title of the document.
|
It is the root of the HTML document which is used to specify that the document is HTML. For example, the Head tag is used to contain all the head element in the HTML file.
|
3.What are the HTML tags used to display the data in the tabular form?
| Tag | Decsription |
<table>
|
It defines a table
|
<tr>
|
This tag defines a row in a table
|
<th>
|
It defines a header cell in a table
|
<td>
|
This is used to define a cell in a table
|
<caption>
|
It defines the table caption
|
<colgroup>
|
It specifies a group of one or more columns in a table for formatting
|
<col>
|
This is used with <colgroup> element to specify column properties for each column
|
<tbody>
|
This tag is used to group the body content in a table.
|
<thead>
|
It is used to group the header content in a table
|
<tfooter>
|
It is used to group the footer content in a table
|
4.How to create a Hyperlink in HTML?
- Unvisited link – It is displayed, underlined and blue.
- Visited link – It is displayed, underlined and purple.
- Active link – It is displayed, underlined and red.
The syntax of Hyperlink in HTML is:
1
| <a href = "..........."> Link Text </a> |
5. Name some common lists that are used when designing a page.
There are many common lists used for design a page. You can choose any or a combination of the following list types:
- Ordered list – The ordered list displays elements in a numbered format. It is represented by <ol> tag.
- Unordered list – The unordered list displays elements in a bulleted format. It is represented by <ul> tag.
- Definition list – The definition list displays elements in definition form like in a dictionary. The <dl>, <dt> and <dd> tags are used to define description list.
6. What is semantic HTML?
Semantic HTML is a coding style. It is the use of HTML markup to reinforce the semantics or meaning of the content. For example: In semantic HTML <b> </b> tag is not used for bold statement as well as <i> </i> tag is used for italic. Instead of these we use <strong></strong> and <em></em> tags.
7. How to create a nested webpage in HTML?
The HTML iframe tag is used to display a nested webpage. In other words, it represents a webpage within a webpage. The HTML <iframe> tag defines an inline frame. For example:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
| <!DOCTYPE html><html><body><h2>HTML example</h2>Use the height and width attributes to specify the size of the iframe:<iframe src="<a href="https://www.edureka.co/">https://www.edureka.co/</a>" height="300" width="400"></iframe></body></html> |
8. What is an image map?
An image map is used for linking many different web pages using a single image. It is represented by <map> tag. You can define shapes in images that you want to include as part of an image mapping.
9. Does a hyperlink only apply to text?
No, hyperlinks can be used both on texts and images. The HTML anchor tag defines a hyperlink that links one page to another page. The “href” attribute is the most important attribute of the HTML anchor tag.
Syntax:
1
| <a href = "..........."> Link Text </a> |
10. What is a Style Sheet?
A style sheet is used to build a consistent, transportable, and well-designed style template. You can add these templates on several different web pages. It describes the look and formatting of a document written in the markup language.
11. Explain the layout of HTML.
HTML layout specifies a way in which the web page is arranged. Every website has a specific layout to display content in a specific manner. Following are different HTML elements which are used to define the different parts of a webpage:
- <header>: It is used to define a header for a document or a section.
- <nav>: This defines a container for navigation links
- <section>: It is used to define a section in a document
- <article>: This is used to define an independent, self-contained article
- <aside>: It is used to define content aside from the content
- <footer>: It is used to define a footer for a document or a section
12. What is a marquee?
Marquee is used for the scrolling text on a web page. It scrolls the image or text up, down, left or right automatically. You should put the text which you want to scroll within the <marquee>……</marquee> tag.
13.What is button tag?
The button tag is used in HTML 5. It is used to create a clickable button within the HTML form on the web page. This tag creates a “submit” or “reset” button. The button tag code is as follows:
1
| <button name="button" type="button">Click Here</button> |
14. List the media types and formats supported by HTML.
HTML supports a wide range of media formats for sound, music, videos, movies, and animations. Some of the extensions supported by each media format are:
- Images– png, jpg, jpeg, gif, apng, svg, bmp, BMP ico, png ico
- Audio– MIDI, RealAudio, WMA, AAC, WAV, Ogg, MP3, MP4
- Video– MPEG, AVI, WMV, QuickTime, RealVideo, Flash, Ogg, WebM, MPEG-4 or MP4
15. What is Cell Spacing and Cell Padding?
Cell Spacing is referred to as the space or gap between the two cells of the same table. Whereas, Cell Padding is referred to as the gap or space between the content of the cell and cell wall or cell border.
Example:
1
2
3
| <table border cellspacing=3><table border cellpadding=3><table border cellspacing=3 cellpadding=3> |
16. What is difference between HTML and XHTML?
The differences between HTML and XHTML are:
- HTML is an application of Standard Generalized Markup Language. Whereas, XML is an application of Extensible Markup Language.
- The first one is a static Web Page whereas the later one is a dynamic Web Page.
- HTML allows programmer to perform changes in the tags and use attribute minimization whereas XHTML when user need a new markup tag then user can define it in this.
- HTML is about displaying information whereas XHTML is about describing the information.
17. How many types of CSS can be included in HTML?
There are three ways to include the CSS with HTML:
- Inline CSS: It is used for styling small contexts. To use inline styles add the style attribute in the relevant tag.
- External Style Sheet: This is used when the style is applied to many pages. Each page must link to the style sheet using the <link> tag. The <link> tag goes inside the head section.
1
2
3
| <head><link rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" href="mystyle.css" /></head> |
- Internal Style Sheet: It is used when a single document has a unique style. Internal styles sheet needs to put in the head section of an HTML page, by using the <style> tag in the following way:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
| <head><style type="text/css">hr {color:sienna}p {margin-left:20px}body {background-image:url("images/back40.gif")}</style></head> |
18. What are logical and physical tags in HTML?
Logical tags are used to tell the meaning of the enclosed text. The example of the logical tag is <strong> </strong> tag. When we enclose the text in the strong tag, it tells the browser that enclosed text is more important than other texts.
Physical tags are used to tell the browser how to display the text enclosed in the physical tag. Some of the examples of physical tags are <b>, <big>, <i>.
19. How can you apply JavaScript to a web page?
In order to make your webpage more interactive, you need JavaScript. It is a scripting language that allows you to interact with certain elements on the page, based on user input. As with CSS, there are three main ways of including JavaScript:
Inline
Certain HTML elements allow you to execute a piece of JavaScript when a certain event occurs. For example, a button allows you to run a script when you click on it. These events are accessed through attributes and differ based on the events that are available on each element. Here is an example that shows an alert with a message when the user clicks on it:










Q #7) Write an HTML code to form a table to show the below values in a tabular form with heading as Roll No., Student name, Subject Name, and values as
1, Ram, Physics
2, Shyam, Math
3, Murli, Chemistry
Ans: To represent the above values in an HTML table format, the code will be:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<style>
table, th, td {
border: 1px solid black;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<table >
<tr>
<th> Roll No. </th>
<th> Student Name </th>
<th> Subject Name </th>
</tr>
<tr>
<td> 1 </td>
<td>Ram</td>
<td> Physics </td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td> 2 </td>
<td> Shyam </td>
<td> Math </td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td> 3 </td>
<td> Murli </td>
<td> Chemistry </td>
</tr>
</table>
</body>
</html>
Output:

Q #8) Define Semantic elements in HTML.
Ans: Semantic elements are HTML elements which represent its meaning to the browser and developer about its contents.
For Example – p tag represents a paragraph, a tag represents anchor tag, form tag, table tag, article tag and many more are semantic elements in HTML. Whereas div tag, span tag, bold tag are not semantic elements.
Q #9) Define attributes in HTML tag.
Ans: The HTML tag contains a field inside their tag which is called attributes of that tag.
For Example:
<img src=”#”> here in this tag src is img tag attributes.
<input type=” text”> here in this tag type is input tag attributes.
Q #10) Can we modify the attribute's value of the HTML tag dynamically?
Ans: Yes, we can modify the value of the attributes by using JavaScript.
Below is the input element whose attribute will be modified from text to password, JS code to modify the attribute value:
<input type=“text” id=“inputField”> document.getElementById(“inputField”).attr(“type”, “password”);
Q #11) How can we comment in HTML?
Ans: Comments are used by developers to keep a track of the code functionality and also help the other developers in understanding the code functionalities easily.
The commented out lines will not be shown in the browser. To comment a line, the line should start by this <!– and end by this –>. Comments can be of one line or of multiple lines.
For Example:
<!-- This is one line comment ? <!-- This is multiple line of two or more line -->
Q #12) What are inline elements and block-level elements in HTML?
Ans: Block elements are the blocks that take the full available width and always start from a new line. It will stretch itself to the full available width of the available container width. Block level elements are <div>, <p>, <img>, <section> and many more.
Inline elements are the elements that will only take the width that is required to fit into the container.
For Example, take the flow of text on the page. When the line of the text takes the full width of the container it wraps itself into a new line and again goes in the same way.
Whereas the inline element will take only that much space or width that it is needed for them. Inline elements are <span>, <label>, <a>, <b> and many more.
Q #13) Can we change inline elements into block-level elements?
Ans: Yes, we can change inline elements into block-level elements by adding display equal to block in its CSS tag. Writing it will change the inline elements into block elements and then inline elements will also take the full width of the container.
display: block;
Q #14) What are the different browsers that support HTML5?
Ans: All modern browsers support HTML5 elements except some old browsers. But fortunately, most of the browsers will take html5 elements as inline elements.
Q #15) What are <br> tags in HTML?
Ans: <br> tags are used to enter a new line into the HTML contents. These tags are generally used to separate two different lines of text between each other.
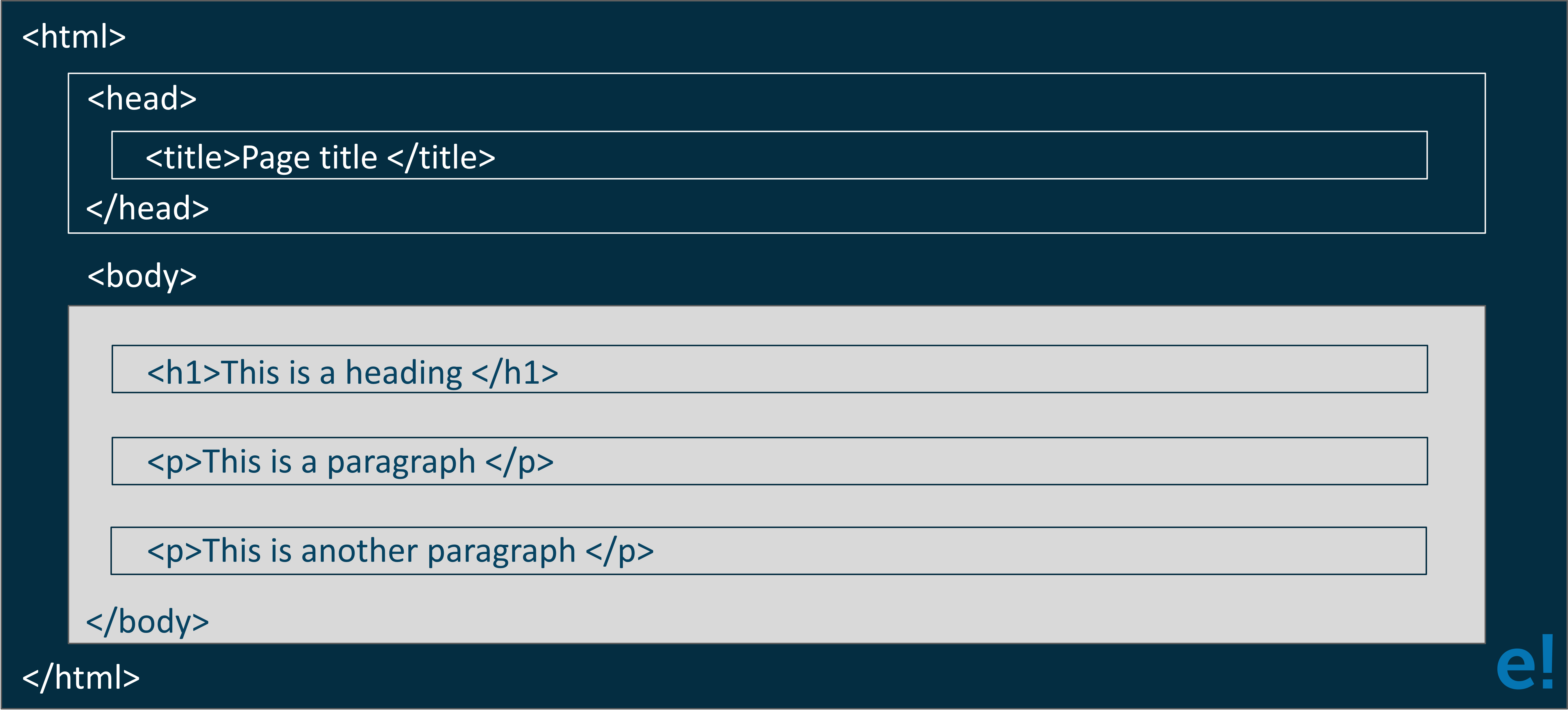
Q #16) Explain the structure of the HTML webpage.
Ans: The common structure which all html pages follow are:
(i) DOCTYPE – It is a special tag in html which is always written at the top of the html document, i.e. at the start of the html template. DOCTYPE is used to convey to the browser about the HTML version.
<!DOCTYPE html>
(ii) HTML – After DOCTYPE tag, html tag is written to start the html template. All the html code will be placed into this html tag. It works as the container for the whole html page elements.
<html> <!-- Rest of the html code will come inside it --> </html>
(iii) HEAD – <head> tag is the first element inside the <html> tag. It is used to provide information to the browser about the page and its contents.
Search Engine Optimization (SEO) techniques are written inside this tag. <title>, <meta> tags are written inside these tag. CSS and JS external links or internal CSS and JS are also written inside this tag.
<head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale = 1.0"> <title>HTML Interview Questions</title> </head>
(iv) BODY – <body> tag are written after the closing tag of the <head> tag, i.e. after </head>. Whatever html code is written inside these tags will be shown by the browser as website content.
<body> <h2>Top HTML Interview Questions</h2> <p>HTML stands for Hypertext Markup Language</p> </body>
All together the whole body will be:
<! DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale = 1.0">
<title>HTML Interview Questions</title>
<style type="text/css">
<!-- CSS Code will be written into these -->
h2{
color: #1855b5;
}
p{
color: #3bd256;
font-weight: 600;
}
</style>
<script type="text/javascript">
<!-- Javascript code will be written into these -->
</script>
</head>
<body>
<h2>Top HTML Interview Questions</h2>
<p>HTML stands for Hypertext Markup Language</p>
</body>
</html>
Output:

Q #17) Why Meta tags are used in HTML?
Ans: Meta tags in html are used by the developer to tell the browser about the page description, author of the template, character set, keywords and many more.
Meta tags are used for search engine optimization to tell the search engine about the page contents.
<meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale = 1.0"> <meta name="description" content="HTML interview questions"> <meta name="author" content="Author Name"> <meta name="copyright" content="All Rights Reserved">
Q #18) Explain list elements in HTML.
Ans. The list elements in HTML are:
- Ordered List (<ol>) – An Ordered List or ol tag are the list which will list the items in an ordered way, i.e. numbered or alphabetically.
- Unordered List (<ul>) – An Unordered List or ul tag is the list which will list the items in an unordered way, i.e. in bulleted format or in any other format.
- Definition List (<dl>) – A definition List or dl tag arranges the items in the way in which they are arranged in a dictionary.
Ordered List:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>HTML Interview Questions Ordered List</title>
</head>
<style>
h1{
color: red;
}
li{
color: #0070ff;
}
</style>
<body>
<h1>Ordered List : </h1>
<ol>
<li>HTML</li>
<li>CSS</li>
<li>Bootstrap</li>
<li>JavaScript</li>
</ol>
</body>
</html>
Output:

Unordered List:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>HTML Interview Questions Unordered List</title>
<style>
h1{
color: red;
}
li{
color: #0070ff;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Unordered List : </h1>
<ul>
<li>HTML</li>
<li>CSS</li>
<li>Bootstrap</li>
<li>JavaScript</li>
</ul>
</body>
</html>
Output:

Definition List:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>HTML Interview Question Definition List</title>
<style>
dt{
font-weight: 600;
font-size: 25px;
color: red;
}
dd{
font-weight: 500;
font-size: 15px;
color: #0070ff;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<dl>
<dt><strong>HTML</strong></dt>
<dd>HTML stands for Hypertext Markup Language</dd>
<dt><bold>CSS</bold></dt>
<dd>CSS stands for Cascading Style Sheets</dd>
</dl>
</body>
</html>
Output:

Q #19) Define iframe in HTML.
Ans: Iframe tag is written as <iframe>.
An iframe is used to display different document content inside the different document content in a rectangular region in the browser. When different document content is embedded into a current HTML content, then it is known as an inline iframe.
The src attribute contains the path to the document that occupies the inline iframe.
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <title>HTML Interview Questions Iframes</title> </head> <body> <p>Iframe HTML Code</p> <iframe src = "demo_iframe.htm" width = "300" height = "300"> Sorry your browser does not support inline frames. </iframe> </body> </html>
Output:

Q #20) Define forms in HTML.
Ans: Forms in html are required when we want to collect the user information whenever a user fills any form or provides any details and when we want to save it into our database.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>HTML Interview Question Form tag</title>
<style>
form {
width: 200px;
border: 2px solid blue;
margin: 0 auto;
padding: 60px 100px;
}
p{
color: red;
font-size: 16px;
font-weight: 600;
}
input::placeholder{
color: blue;
}
button{
line-height: 20px;
text-align: center;
background: green;
border: 0;
color: #ffffff;
font-size: 14px;
padding: 15px 64px;
margin-top: 20px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<form >
<p>Name:</p>
<input type = "text" name = "user_name" placeholder = "Enter Name"/>
<br/>
<br/>
<p>Email: </p>
<input type = "email" name = "user_email" placeholder = "Enter email"/>
<br/>
<br/>
<p>Password: </p>
<input type="password" name = "user_pwd" placeholder = "Enter Password" />
<br/>
<button> Submit </button>
</form>
</body>
</html>
Output:

Q #21) In how many ways can a heading be written in HTML?
Ans: A heading is a block level element which is used to give a heading to the particular section or topic.
A total of 6 types of headings can be written in HTML:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<style>
h1{
color: red;
}
h2{
color: blue;
}
h3{
color : green;
}
h4{
color: purple;
}
h5{
color: yellow;
}
h6{
color: orange;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Heading 1</h1>
<h2>Heading 2</h2>
<h3>Heading 3</h3>
<h4>Heading 4</h4>
<h5>Heading 5</h5>
<h6>Heading 6</h6>
</body>
</html>
Output:

Q #22) How can we create a hyperlink in HTML?
Ans: An anchor tag or <a> tag in HTML is used to create hyperlinks which create a path between two different HTML web pages.
Hyperlinks can be displayed in three ways:
- Unvisited Link – These links are blue in color and underlined.
- Visited Link – These links are purple in color and underlined.
- Active Link – These links are red in color and underlined.
Q #23) Why do we use the required attribute in HTML?
Ans: The required attribute is used in HTML to make the field mandatory. It forces the user to fill that particular field to submit the form.
If the field is input then it will throw a default HTML error.
<input type="email" name = "user_email" required />
Q #24) How can we include Google maps on a website?
Ans: HTML Google maps allow us to display Google maps on our web page:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<h1>HTML Interview Questions Google Map</h1>
<div id="map" style="width: 400px; height: 400px; background: yellow">
</div>
<script>
function myMap() {
var mapOptions = {
center: new google.maps.LatLng(51.5, -0.12),
zoom: 10
}
var map = new google.maps.Map(document.getElementById("map"), mapOptions);
}
</script>
<script src= "https://maps.googleapis.com/maps/api/js?key=AIzaSyBu-916DdpKAjTmJNIgngS6HL_kDIKU0aU&callback=myMap"></script>
</body></html>
Output:

Q #25) Differentiate between HTML and XHTML.
Ans: Below are the differences between HTML and XHTML:
- HTML stands for Hypertext Markup Language, whereas XHTML stands for Extensible Markup Language.
- A static webpage is an html web page and dynamic web pages are XHTML.
- XHTML are more stricter than HTML.
- An XML application of HTML is defined as XHTML.
- All modern browsers support XHTML.
Q #26) What is Web Workers?
Ans: Web Workers is a code of JavaScript which runs in the background threads without disturbing the performance of the page. It is used for computing-heavy tasks like an access database or function.
Q #27) What is the SVG element?
Ans: SVG is a followed XML format; it stands for Scalable Vector Graphics which is used to create vector graphics with the support for interactivity and animation.
SVG is resolution independent as it’s not losing its quality when they are resized or zoomed.
Q #28) Explain about Canvas.
Ans: Canvas is a pixel-based graphics and it is one of the new features of HTML5.
It provides a space in the document where we can draw graphics by using JavaScript and it is resolution dependent, hence the quality will be affected when it's zoomed or resized.
Example:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<canvas id="myCanvas" width="300" height="200" style="border:1px solid #d3d3d3; color: #c9cc18;">
Your browser does not support the HTML5 canvas tag.</canvas>
<script>
var can = document.getElementById("myCanvas");
var canvas = can.getContext("2d");
canvas.font = "20px Hind-sanserif";
canvas.fillText("Canvas Example",30,60);
</script>
</body>
</html>

Q #29) Explain new form elements in HTML5.
Ans: The new form elements that were added into HTML5 are:
- Datalist – It’s used as a list of options for input control.
- Keygen – This tag defines a key-pair generator (Private/Public) field.
- Output – It’s used to show the result of a calculation.
Q #30) What is Quirks mode in HTML5?
Ans: If we do not include the <!DOCTYPE> element in our HTML page or Document, it will go to Quirks Mode. In this mode, the HTML element depends on the browser.
Hence the content will be displayed according to the browser.